Havasu Falls
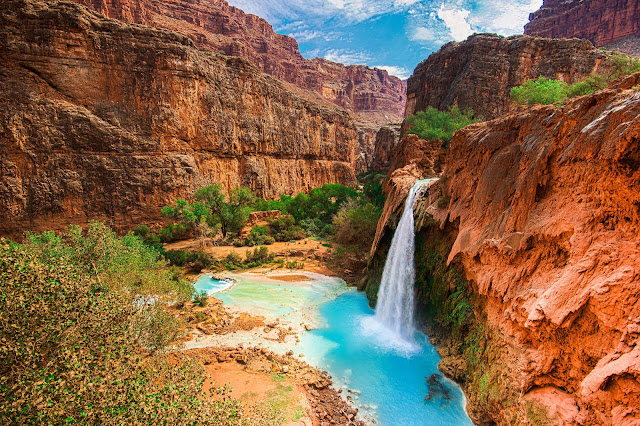

Havasu Falls is a waterfall of Havasu Creek, located in the Grand Canyon, Arizona, United States. It is within Havasupai tribal lands. Havasu Falls is located 1 1⁄2 miles (2.4 km) from Supai. It is the more famous and most visited of the various falls along Havasu Creek. It consists of one main chute that drops over a 90-to-100-foot (27 to 30 m) vertical cliff into a series of plunge pools. High calcium carbonate concentration in the water creates the vivid blue-green color and forms the natural travertine dams that occur in various places near the falls. Due to the effects of flash floods, the appearance of Havasu Falls and its plunge pools has changed many times. Prior to the flood of 1910, water flowed in a near continuous sheet, and was known as Bridal Veil Falls. The notch through which water flows first appeared in 1910, and has changed several times since. Water currently flows as one stream. In the past, there were sometimes multiple streams, or a continuous flow over the edge.