ALMA’s Most Detailed Image of a Protoplanetary Disc - Evidence for planet formation in Earth-like orbit around young star
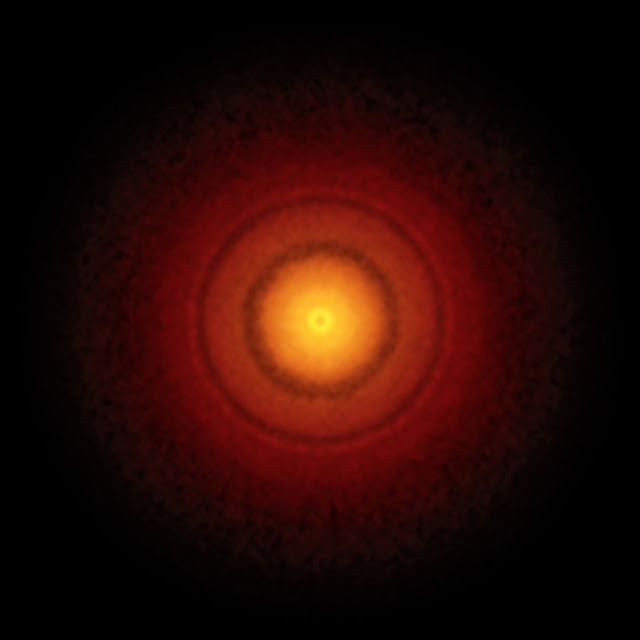
This new image from the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA) shows the finest detail ever seen in the planet-forming disc around the nearby Sun-like star TW Hydrae. It reveals a tantalising gap at the same distance from the star as the Earth is from the Sun, which may mean that an infant version of our home planet, or possibly a more massive super-Earth, is beginning to form there.
The star TW Hydrae is a popular target of study for astronomers because of its proximity to Earth (only about 175 light-years away) and its status as an infant star (about 10 million years old). It also has a face-on orientation as seen from Earth. This gives astronomers a rare, undistorted view of the complete protoplanetary disc around the star.
"Previous studies with optical and radio telescopes confirm that TW Hydrae hosts a prominent disc with features that strongly suggest planets are beginning to coalesce," said Sean Andrews with the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics in Cambridge, Massachusetts, USA and lead author on a paper published today in the Astrophysical Journal Letters. "The new ALMA images show the disc in unprecedented detail, revealing a series of concentric dusty bright rings and dark gaps, including intriguing features that may indicate that a planet with an Earth-like orbit is forming there."
Other pronounced gaps that show up in the new images are located three billion and six billion kilometres from the central star, similar to the average distances from the Sun to Uranus and Pluto in the Solar System. They too are likely to be the results of particles that came together to form planets, which then swept their orbits clear of dust and gas and shepherded the remaining material into well-defined bands.
For the new TW Hydrae observations, astronomers imaged the faint radio emission from millimetre-sized dust grains in the disc, revealing details on the order of the distance between the Earth and the Sun (about 150 million kilometres). These detailed observations were made possible with ALMA’s high-resolution, long-baseline configuration. When ALMA's dishes are at their maximum separation, up to 15 kilometres apart, the telescope is able to resolve finer details. "This is the highest spatial resolution image ever of a protoplanetary disc from ALMA, and that won't be easily beaten in the future!" said Andrews.
"TW Hydrae is quite special. It is the nearest known protoplanetary disc to Earth and it may closely resemble the Solar System when it was only 10 million years old," adds co-author David Wilner, also with the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics.
Earlier ALMA observations of another system, HL Tauri, show that even younger protoplanetary discs — a mere 1 million years old — can display similar signatures of planet formation. By studying the older TW Hydrae disc, astronomers hope to better understand the evolution of our own planet and the prospects for similar systems throughout the Milky Way.
The astronomers now want to find out how common these kinds of features are in discs around other young stars and how they might change with time or environment.
Image Credit: S. Andrews (Harvard-Smithsonian CfA); B. Saxton (NRAO/AUI/NSF); ALMA (ESO/NAOJ/NRAO)
Explanation from: http://www.eso.org/public/news/eso1611/


Comments
Post a Comment